 Bladder cancer biomarker signature could identify likely responders to checkpoint inhibitors
Bladder cancer biomarker signature could identify likely responders to checkpoint inhibitors
Scientists have found signatures associated with the response of bladder cancer to immune checkpoint inhibitors, suggesting that it may be possible to molecularly stratify patients to increase response rates. Read More
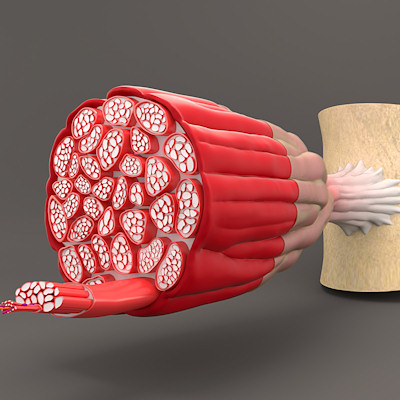 Researchers modify lentivirus to enable targeted delivery of muscle disease gene therapy
Researchers modify lentivirus to enable targeted delivery of muscle disease gene therapy
Researchers have created a lentiviral gene therapy vector capable of targeting muscle cells to treat the rare disease Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in mice. Read More
 Reanalysis of old data reveals overlooked liver gene therapy vector with better properties
Reanalysis of old data reveals overlooked liver gene therapy vector with better properties
Rational design and directed evolution have created an adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid that is better at targeting the liver, setting the stage for its use as a gene therapy vector. Read More
 Targeting viral RNA to treat infection
Targeting viral RNA to treat infection
Despite the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines, the rise of variants forces scientists to frequently modify treatments. A new study published Wednesday in ACS Central Science describes a treatment that directly targets and degrades the viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) genome, reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. Read More
 Inflammatory gene variant protects mice from kidney problems, pointing to new diagnostic tool
Inflammatory gene variant protects mice from kidney problems, pointing to new diagnostic tool
The discovery of a variant of an inflammatory gene that protects the kidneys in mice could unlock more personalized approaches to the treatment of humans. Read More
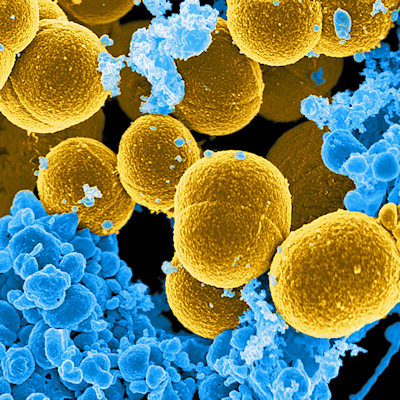 Bioengineered drug fights Staphylococcus infection
Bioengineered drug fights Staphylococcus infection
Early tests show that a bioengineered drug can counter infection with Staphylococcus aureus, a major cause of death in hospital patients. The research, published Monday in Cell Host & Microbe, demonstrated that the antibacterial biologic agent was superior to standard antibiotic drugs at treating S. aureus-infected mice, including its treatment-resistant form methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Read More
 Study uncovers novel biomarker and potentially improved therapy for multiple sclerosis
Study uncovers novel biomarker and potentially improved therapy for multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and related neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease, affect about 2.8 million people worldwide. MS, an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells, has specific hallmarks, including neuroinflammation and the degeneration of myelin, an insulating sheath required for rapid nerve-cell communication. Research published Thursday in Cell Metabolism describes how myelin breakdown results in the accumulation of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA), which triggers this damaging response. Read More
 Infectious SARS-CoV-2 found in hospital air
Infectious SARS-CoV-2 found in hospital air
Quebec researchers isolated infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus particles from air samples that were originally collected from COVID-19 patients’ hospital rooms, then kept frozen for more than a year. Read More
 Emergency brake keeps bladder cells from turning cancerous
Emergency brake keeps bladder cells from turning cancerous
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center scientists discovered an emergency brake that bladder cells use to ward off tumors even when cancer-promoting genes are turned on. In a study published April 20 in Cancer Cell, the scientists halted human bladder tumor growth in mice, suggesting the brake could be a target for future bladder cancer therapies. Read More
 Engineered stem cells clear barrier to potential one-time treatment of ALS
Engineered stem cells clear barrier to potential one-time treatment of ALS
Researchers have used human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to overcome a barrier to the supply of a potential treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and retinitis pigmentosa. Read More
Conferences
Science Briefs
Member Rewards
Earn points for contributing to market research. Redeem your points for merchandise, travel, or even to help your favorite charity.
Research Topics
Interact with an engaged, global community of your peers who come together to discuss their work and opportunities.
Connect
Tweets by @ScienceBoard






